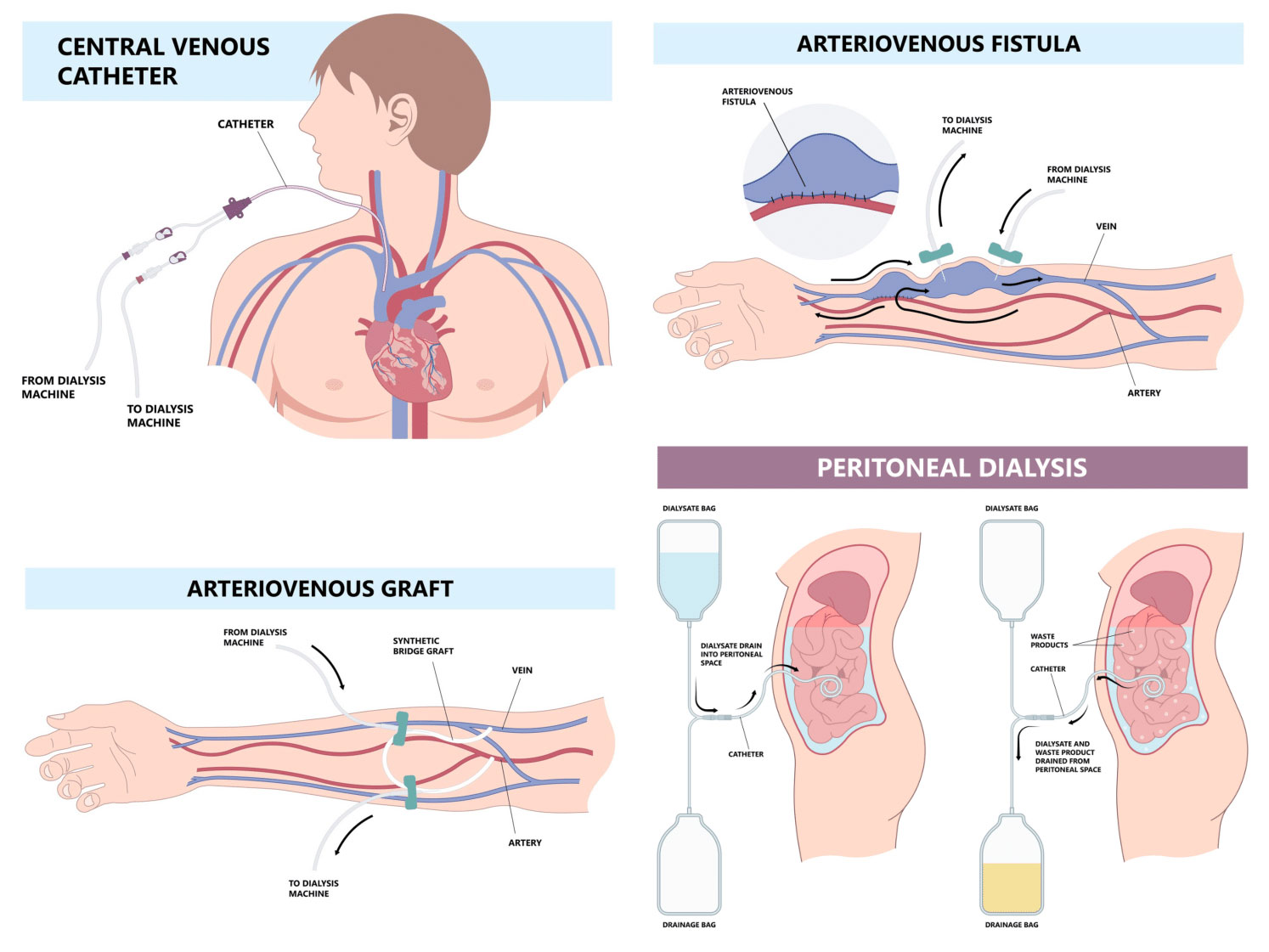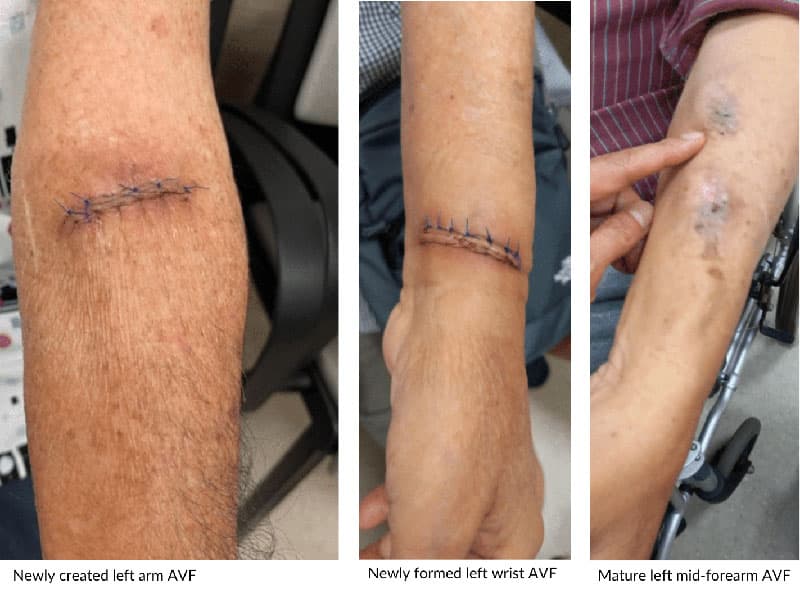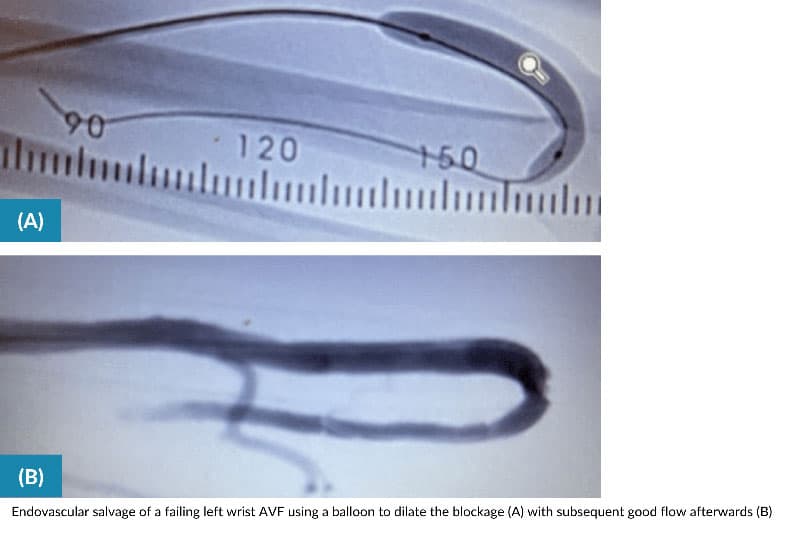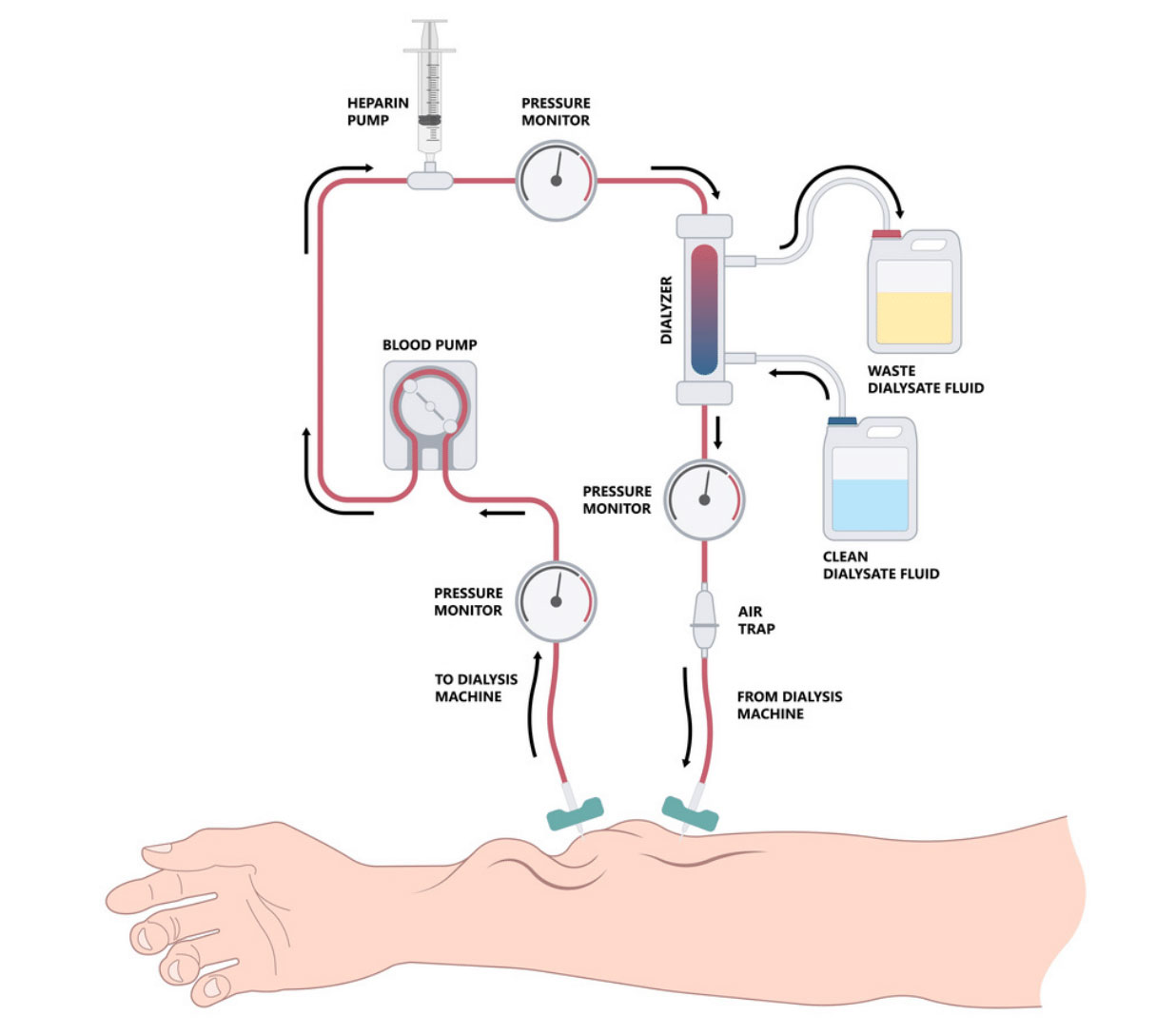
What is Dialysis Access Creation
You may already know that before you can receive dialysis, you need to have an access placed. Your dialysis access is your lifeline and a critical factor in enabling you to obtain the best dialysis treatment possible. Gaining an understanding of the 4 types of dialysis access will help you determine which type of dialysis access is right for you. Which access is the best for you will depends on many factors and a detailed discussion should occur between you and your vascular specialist before deciding which route to take.
Haemodialysis is a method in which a tube is inserted into a patient’s bloodstream to allow blood to travel from your body to the dialysis machine, where it can be cleaned and returned back into the bloodstream.