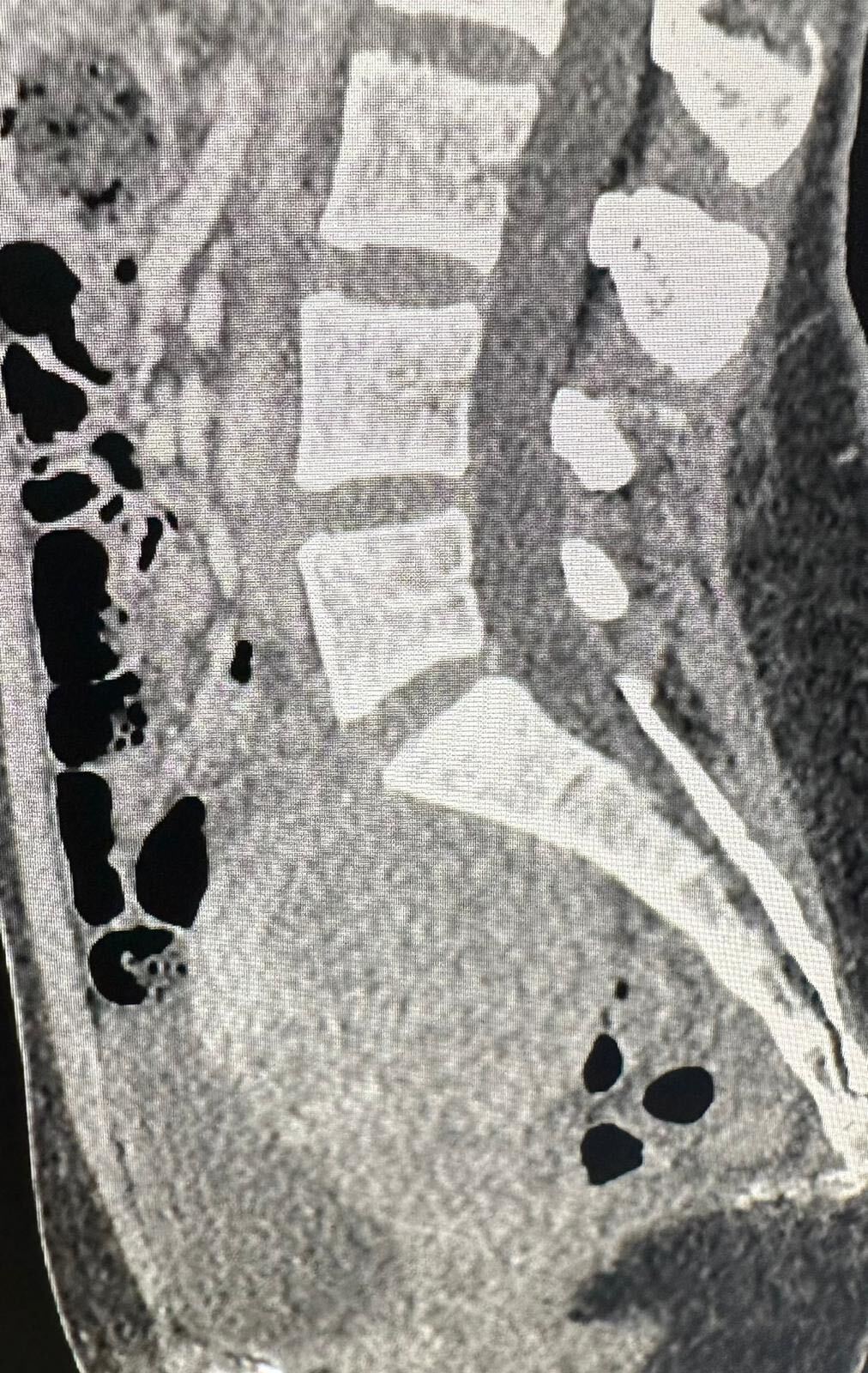
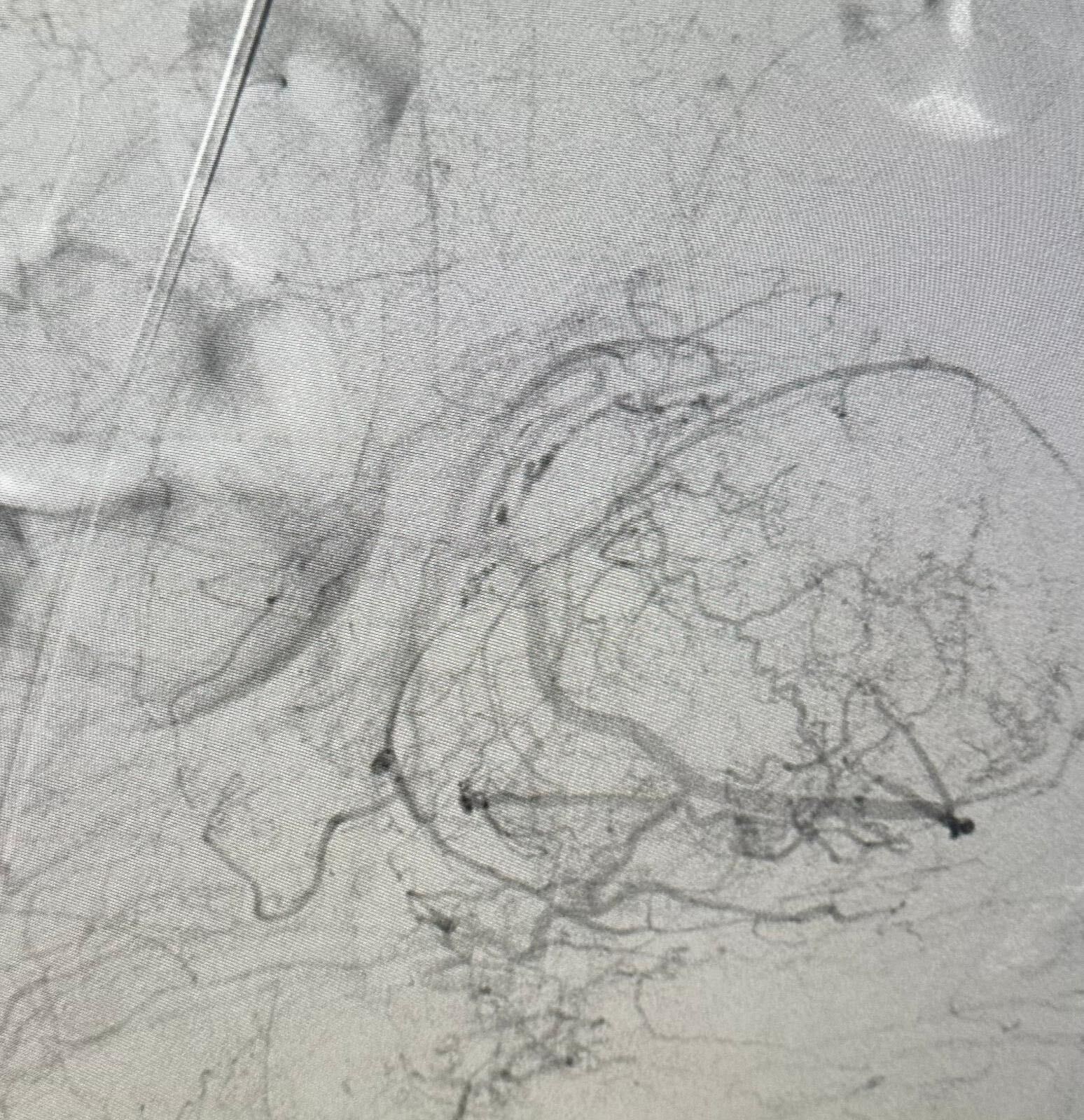
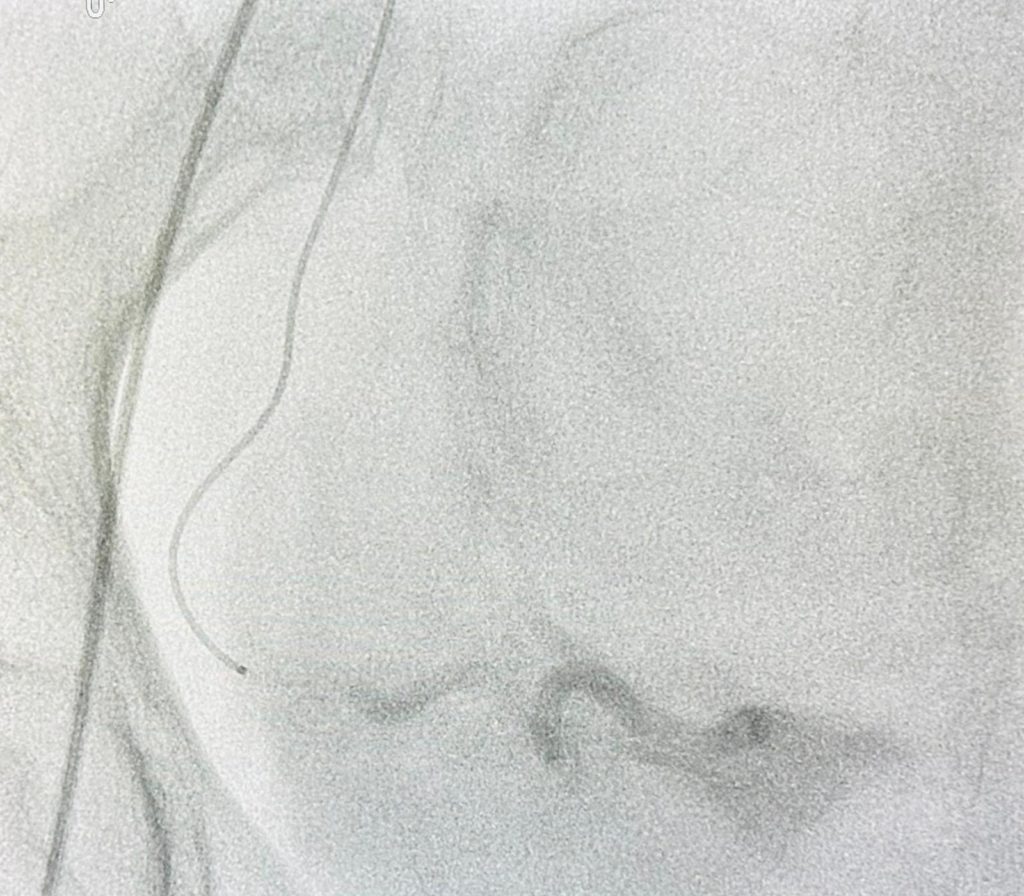
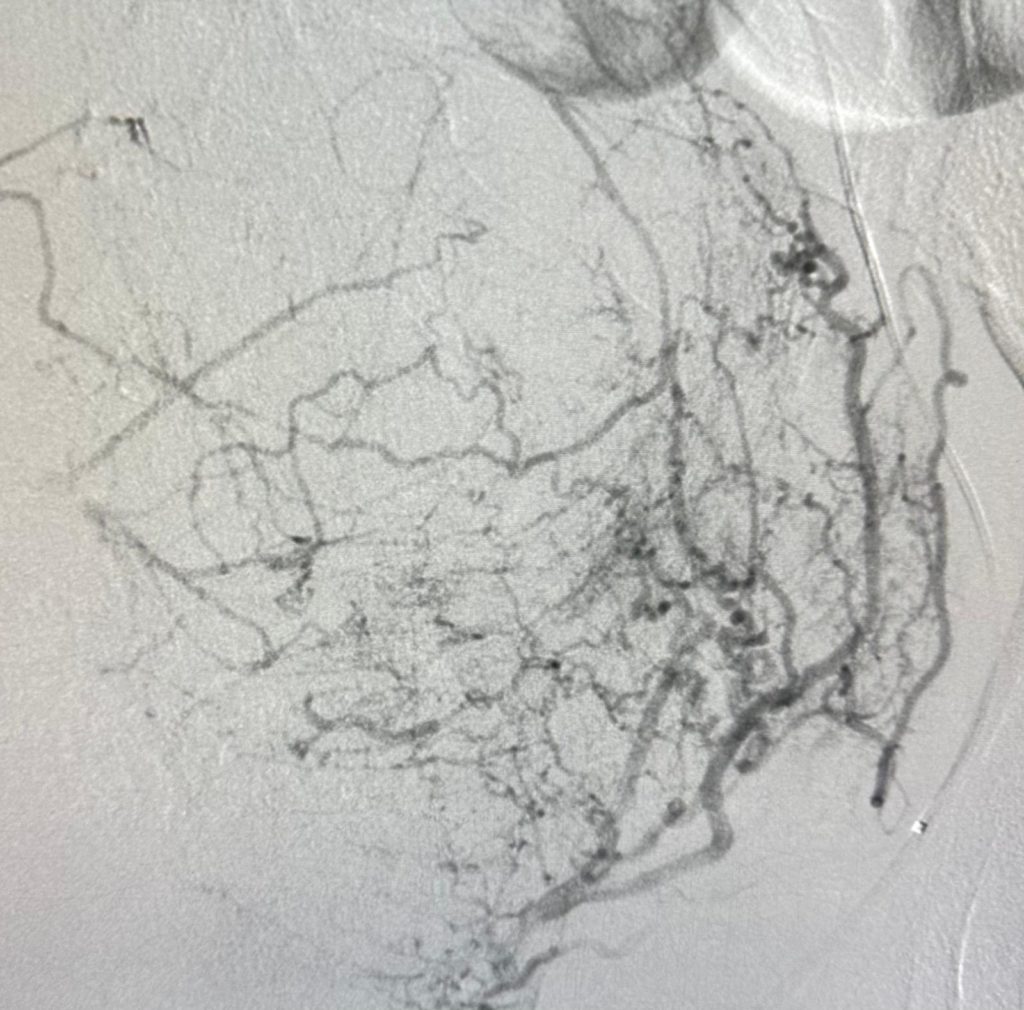
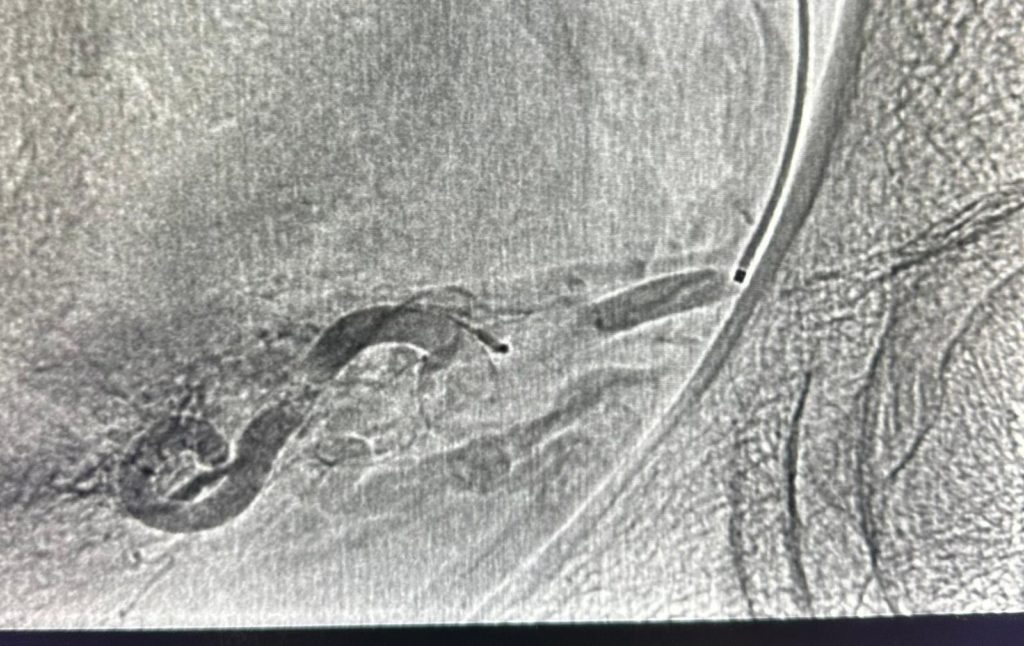
What are fibroids?
Fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They are also known as uterine fibroids or leiomyomas. Fibroids are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size. They can be as small as a seed or as large as a grapefruit. Fibroids can be single or multiple and may grow inside the uterus, on the outer surface of the uterus, or within the uterine wall. They are quite common, with about 70-80% of women developing fibroids by the age of 50.