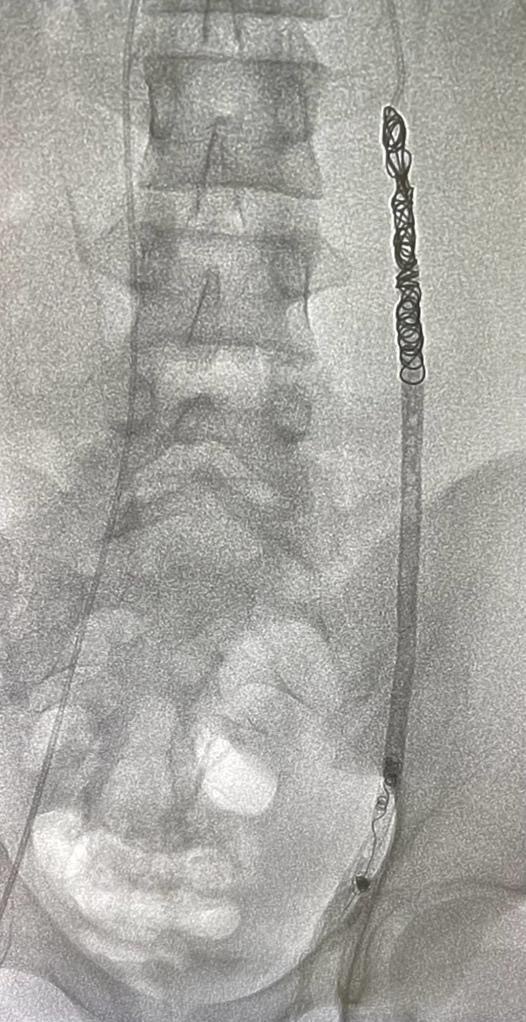
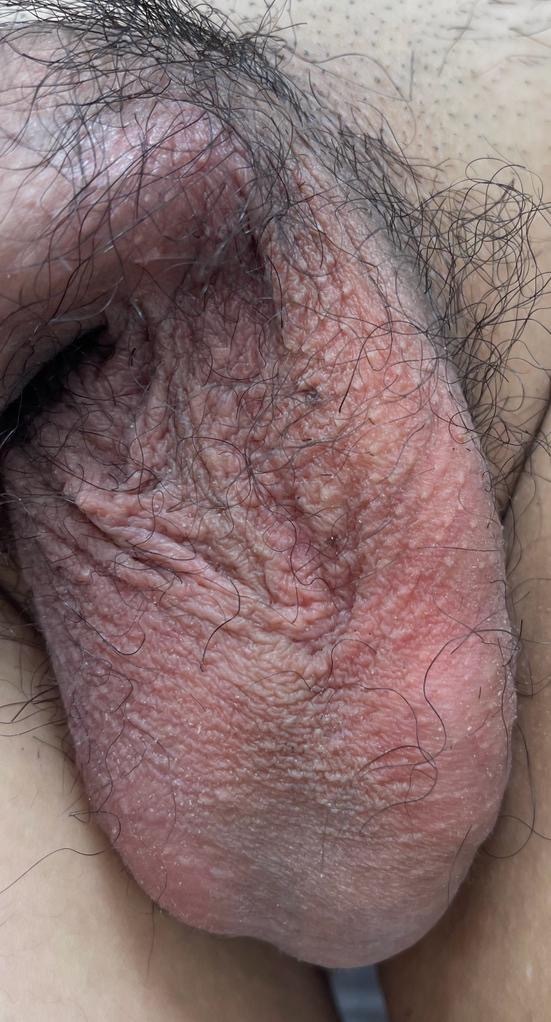
Varicocoeles?
A varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the loose bag of skin that holds your testicles (scrotum). It’s similar to a varicose vein you might see on your leg. Varicoceles are a common cause of low sperm production and decreased sperm quality, which can cause infertility.