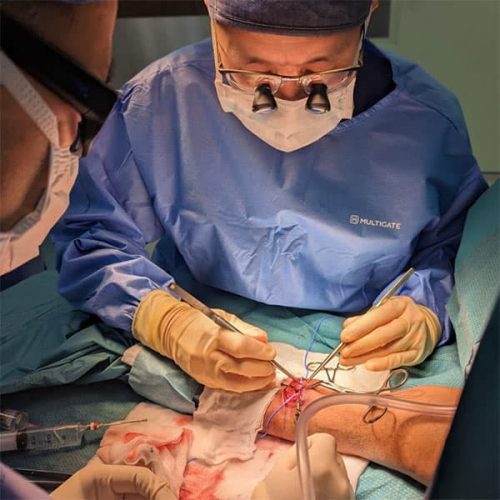
The AVF is created by connecting an artery to a vein, which creates a larger and stronger vein that can withstand the repeated needle insertions required for hemodialysis. The connection is typically made in the arm, although other sites may be used as well. The AVF allows for a greater blood flow rate during hemodialysis, increasing treatment efficiency and reducing the risk of complications such as infection or clotting.
An AVF typically takes 6-8 weeks to mature before it can be used for hemodialysis. During this time, it is important to protect the site from injury and avoid activities that could put stress on the connection. Once the AVF has matured, it can be used for hemodialysis on a regular basis.
One of the benefits of an AVF is that it can last for many years, reducing the need for multiple surgeries to create new access sites. It also has a lower risk of complications such as infection or clotting compared to other types of access sites.
The AVF is created by connecting an artery to a vein, which creates a larger and stronger vein that can withstand the repeated needle insertions required for hemodialysis. The connection is typically made in the arm, although other sites may be used as well. The AVF allows for a greater blood flow rate during hemodialysis, increasing treatment efficiency and reducing the risk of complications such as infection or clotting.
An AVF typically takes 6-8 weeks to mature before it can be used for hemodialysis. During this time, it is important to protect the site from injury and avoid activities that could put stress on the connection. Once the AVF has matured, it can be used for hemodialysis on a regular basis.
One of the benefits of an AVF is that it can last for many years, reducing the need for multiple surgeries to create new access sites. It also has a lower risk of complications such as infection or clotting compared to other types of access sites.
However, there are some risks associated with an AVF. The most common complication is the development of stenosis, or narrowing, at the site of the connection. Stenosis can reduce blood flow and make it more difficult to perform hemodialysis. It can usually be treated with a procedure called angioplasty, which involves inflating a small balloon at the site to widen the narrowed area.
In rare cases, an AVF can also develop an aneurysm or a bulging of the blood vessel at the site of the connection. This can be a serious complication and may require surgery to repair.
Overall, an AVF is a common and important surgical procedure for patients with end-stage renal disease who require hemodialysis. It provides a durable and efficient access site for hemodialysis, although it does carry some risks that should be carefully monitored and managed.
It is highly recommended to consult with a vascular surgeon to determine the suitability of an AVF. They will tailor a personalized treatment plan based on your health condition and medical history, ensuring the best course of action for your specific needs.