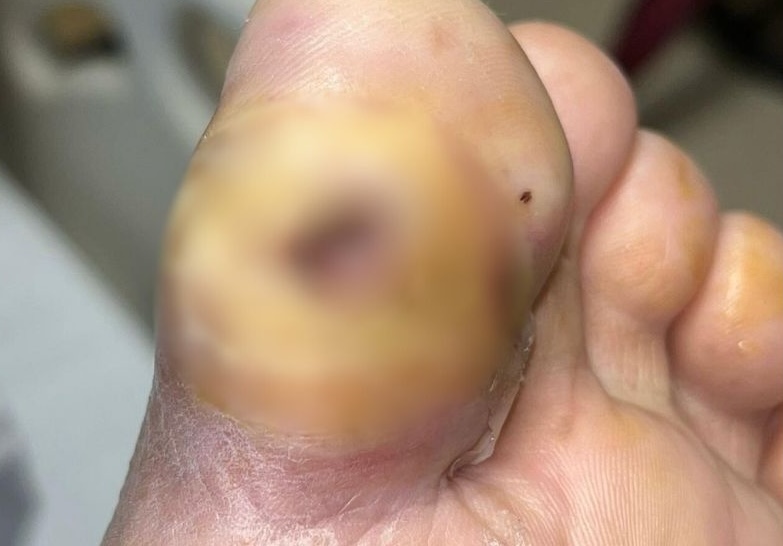
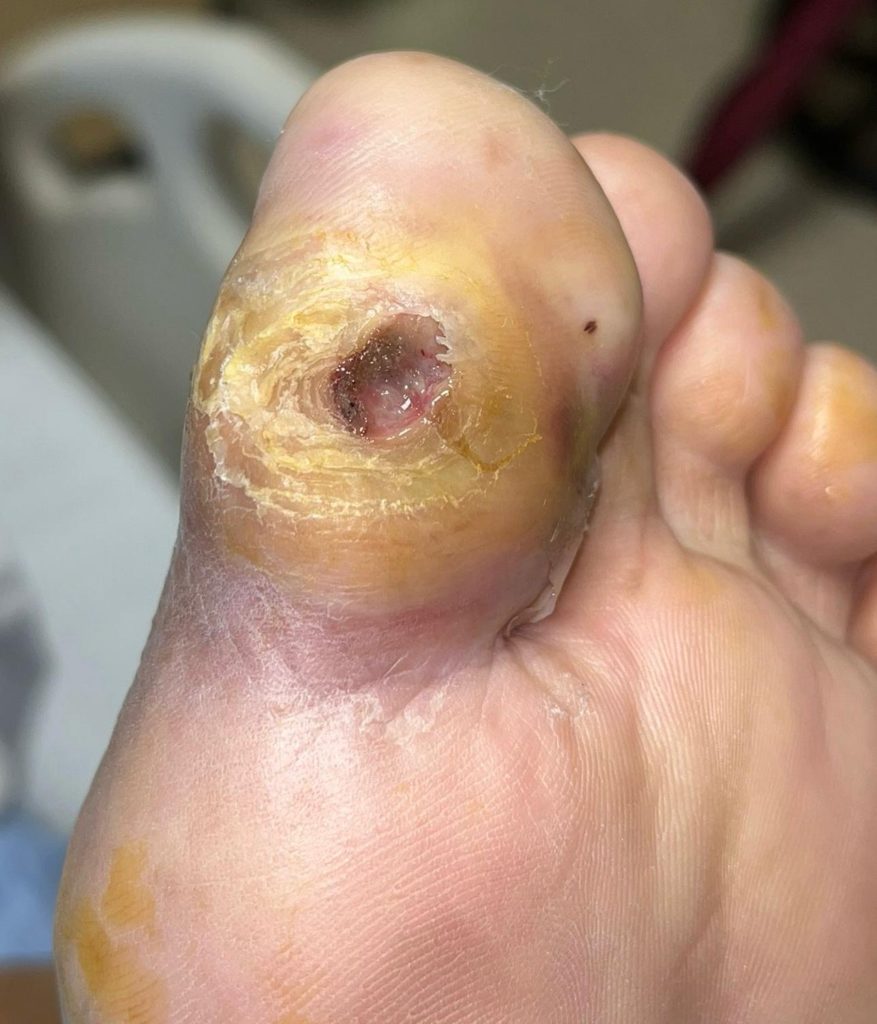
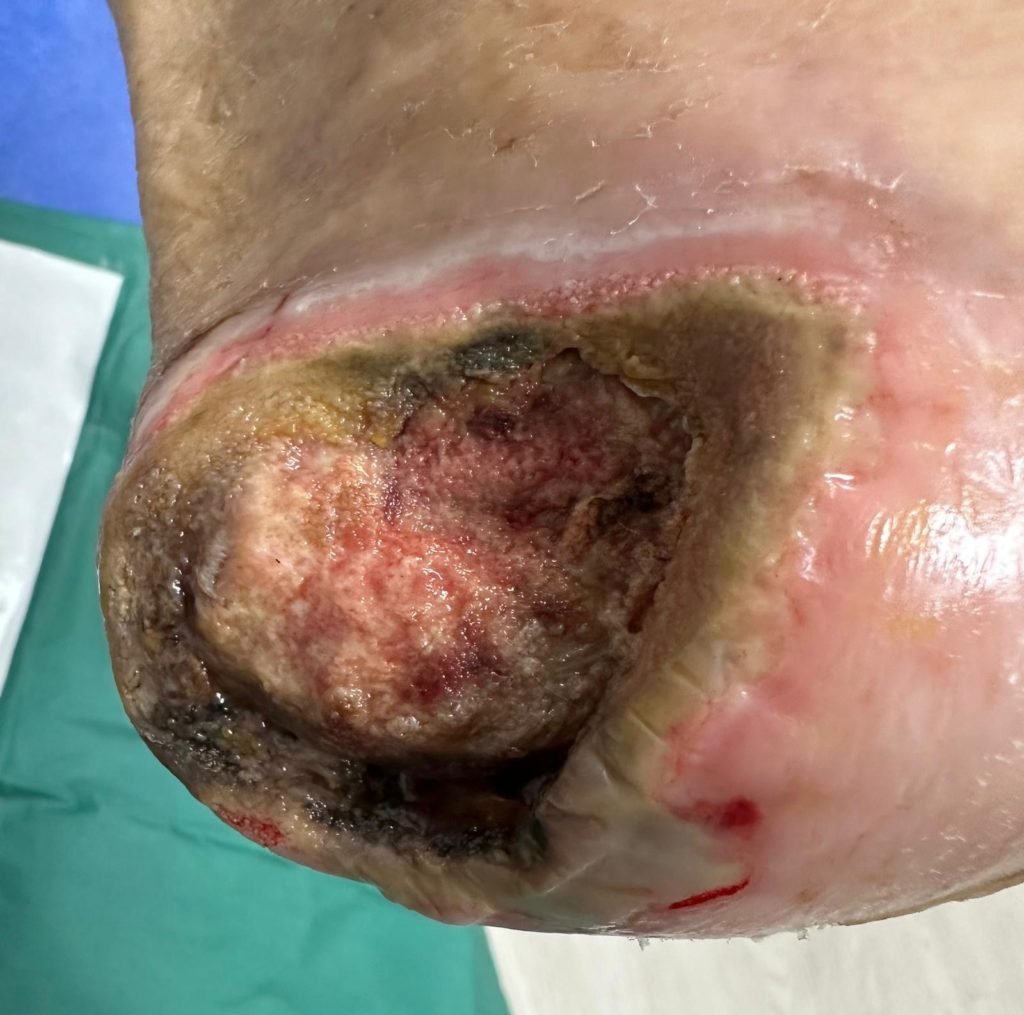
You should see a vascular specialist for a diabetic foot ulcer if you experience any of the following:
- The ulcer does not heal within two weeks.
- The ulcer becomes infected.
- There is an increase in pain or swelling.
- You notice any signs of cellulitis (redness, warmth, and tenderness in the surrounding skin).
- You develop a fever or chills.
- You have poor circulation or nerve damage in your feet.
- You have a history of foot ulcers or complications related to diabetes.
Several factors can affect the prognosis of a diabetic foot ulcer. These include:
- Duration: The longer a diabetic foot ulcer remains untreated or unhealed, the poorer the prognosis. Prompt medical attention and early intervention can significantly improve the chances of successful healing.
- Size and Depth: The size and depth of the ulcer can also influence the prognosis. Larger and deeper ulcers are typically more difficult to heal and may require more intensive treatment.
- Infection: If a diabetic foot ulcer becomes infected, it can significantly impact the prognosis. Infections can delay healing and increase the risk of complications. Prompt and appropriate management of infections is essential for a better prognosis.
- Underlying Health Conditions: The presence of underlying health conditions, such as poor circulation (peripheral arterial disease) or peripheral neuropathy, can negatively affect the prognosis of a diabetic foot ulcer. These conditions can impair the body’s ability to heal and increase the risk of complications.
- Glycemic Control: Poorly controlled blood sugar levels (high or low) can impair wound healing and negatively impact the prognosis of a diabetic foot ulcer. Maintaining good glycemic control is crucial for optimal healing.
- Patient Compliance: The patient’s ability to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan, including wound care, off-loading, and lifestyle modifications, can significantly influence the prognosis. Compliance with medical advice and regular follow-up appointments is important for successful healing.
- Medical Intervention: The type and quality of medical intervention received can also affect the prognosis. Specialized wound care, appropriate use of dressings, off-loading devices, and other interventions recommended by your vascular surgeon can improve the chances of healing and prevent complications.
- Overall Health and Nutritional Status: The patient’s overall health and nutritional status play a role in wound healing. Adequate nutrition, a healthy immune system, and good general health can positively impact the prognosis.
It is important to note that every individual and every diabetic foot ulcer is unique, and the prognosis can vary depending on multiple factors. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in diabetic foot care can provide a more accurate assessment of the prognosis and guide appropriate treatment.
It is important to note that every individual and every diabetic foot ulcer is unique, and the prognosis can vary depending on multiple factors. Consulting with a vascular surgeon who specializes in diabetic foot care can provide a more accurate assessment of the prognosis and guide appropriate treatment.
The treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer typically involves a combination of different approaches, which may include:
- Wound care: Proper wound care is essential for healing a diabetic foot ulcer. This may involve cleaning the wound, removing dead tissue, and applying appropriate dressings.
- Offloading: Offloading refers to relieving pressure on the affected foot or ulcer site. This can be achieved through the use of specialized footwear, casts, or orthotic devices to redistribute weight and reduce pressure on the ulcer.
- Infection control: If there is an infection present, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and prevent its spread. It is important to closely monitor and manage any signs of infection.
- Blood sugar control: Maintaining good control of blood sugar levels is crucial in promoting wound healing. This may involve adjustments to diet, medication, or insulin therapy as recommended by a healthcare professional.
- Debridement: Debridement is the removal of dead or infected tissue from the wound. This can help promote healing and prevent the spread of infection.
- Topical medications: Depending on the specific characteristics of the ulcer, healthcare professionals may recommend the use of topical medications such as antimicrobial creams or ointments to aid in healing.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: In some cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be recommended. This involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which can promote faster healing by increasing the oxygen supply to the tissues.
- Surgical intervention: In more severe cases or when conservative treatments are not effective, surgical intervention may be necessary. This can involve procedures such as wound closure, skin grafts, or the removal of infected tissue.
The role of improving blood supply to the wound:
Improving blood supply is a crucial factor in healing a diabetic foot ulcer. Inadequate blood flow to the affected area can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Here are some ways in which improving blood supply can contribute to the healing of a diabetic foot ulcer:
- Enhanced oxygen and nutrient delivery: Adequate blood supply brings oxygen and essential nutrients to the wound site, which are necessary for the healing process. Oxygen plays a vital role in cellular metabolism and promotes the growth of new tissue. Nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and vitamins are also required for cellular repair and regeneration.
- Removal of waste products: Improved blood circulation helps in the efficient removal of waste products from the wound, such as dead tissue, bacteria, and toxins. Proper waste removal fosters a clean and favourable environment for healing.
- Immune response activation: Blood carries immune cells to the wound site, which are crucial in fighting infection and promoting wound healing. Improved blood flow helps in the recruitment of immune cells, enhancing the body’s defence mechanisms against infection.
- Collagen synthesis: Collagen, a protein that provides structural support to the skin, is essential for wound healing. Adequate blood supply promotes collagen synthesis, which helps in the formation of new tissue and the closure of the ulcer.
To improve blood supply to a diabetic foot ulcer, a vascular surgeon may recommend several approaches, including:
- Offloading: Relieving pressure on the foot ulcer helps improve blood flow to the area. This can be achieved through the use of specialized footwear, casts, or orthotic devices.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, as advised by a healthcare professional, can help improve overall blood circulation and promote healing.
- Vascular interventions: In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be recommended to restore blood flow to the affected area.
- Medications: Medications that improve blood flow, such as vasodilators or antiplatelet drugs, may be prescribed to enhance circulation.