Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) access surgery refers to creating a connection between an artery and a vein in the body, usually in the arm, to allow for easier and more efficient hemodialysis treatment for patients with kidney failure.
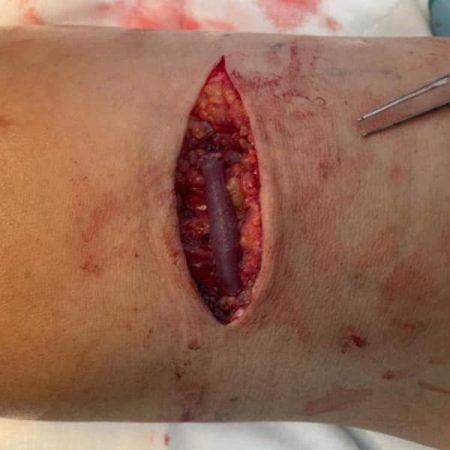
The picture above shows a brachiocephalic fistula creation at the elbow crease. The AVF cannot be used immediately and usually takes 6-8 weeks to mature before it can start being cannulated.
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) access surgery refers to creating a connection between an artery and a vein in the body, usually in the arm, to allow for easier and more efficient hemodialysis treatment for patients with kidney failure. This type of surgery is typically performed by a vascular surgeon and involves connecting a vein and artery together to create a larger, stronger blood vessel, which can withstand the needling process for HD 3 times a week. The arteriovenous fistula access site is then used for dialysis treatment, where blood is removed from the patient’s body, filtered through a machine, and returned to the body.
AVF is considered the gold standard for hemodialysis because it provides the best long-term vascular access for patients receiving hemodialysis. It is preferred over other types of vascular access, such as arteriovenous grafts (AVGs) and central venous catheters (CVCs), due to its lower risk of complications, including infection and clotting.
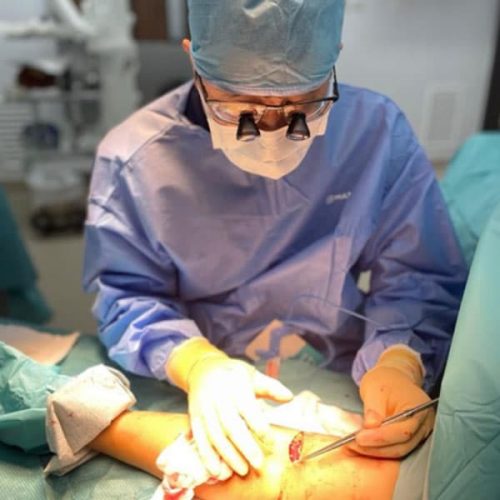
An arteriovenous fistula is also associated with better long-term outcomes, such as lower rates of hospitalization, lower mortality rates, and a lower risk of cardiovascular events compared to other types of vascular access methods. Additionally, an arteriovenous fistula is cost-effective, as it does not require regular maintenance and has a longer lifespan than AVGs and CVCs.
It is important to note that an arteriovenous fistula cannot be used immediately after it is created. It takes several weeks or even months for it to mature and become suitable for hemodialysis. After the arteriovenous fistula is created, it requires time for it to develop a sufficient blood flow and for the veins to enlarge and become strong enough to withstand the high blood flow rate required for hemodialysis. During this time, patients may need to continue using other forms of vascular access, such as a CVC, until the arteriovenous fistula matures and is ready for use.
The amount of time required for an arteriovenous fistula to mature can vary depending on the patient’s individual circumstances, including their age, overall health, and the location of the arteriovenous fistula. It is important for patients to follow their vascular surgeon’s instructions and attend all follow-up appointments to ensure their arteriovenous fistula is properly monitored and ready for use when it is deemed mature.
A nerve block may be used during an arteriovenous fistula creation procedure to help manage pain and discomfort during and after the procedure. It can also help dilate an otherwise small vein and help procedural success during the joining of the vein to the artery. An arteriovenous fistula creation under a nerve block and sedation is considered the gold standard of care and patients generally have a better experience than if the AVF was created under pure local anaesthetic.
During a nerve block, a local anaesthetic medication is injected around the nerves that transmit pain signals from the area being operated on. This numbs the area and helps reduce pain and discomfort.
Nerve blocks are generally safe and effective, but like any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. These may include bleeding, infection, nerve damage, or an allergic reaction to the anesthetic medication. However, these are rare in experienced hands. Your vascular surgeon will discuss the potential risks and benefits of a nerve block with you before the procedure.
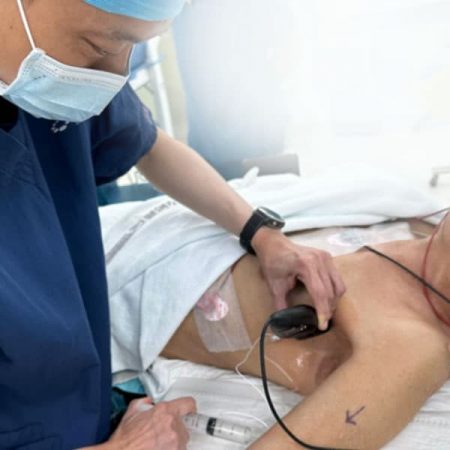
The picture above shows Dr Jimmy Phoo, one of The VEC’s regular and highly experienced AVF anesthetists, doing a cervical nerve block prior to an arteriovenous fistula creation.
In summary, the arteriovenous fistula (AVF) access surgery is a highly effective method to improve hemodialysis treatment as it allows for better results, fewer complications, and a more convenient experience during hemodialysis. Patients can benefit from improved health outcomes, reduced risks, and greater ease in their hemodialysis treatment.









