What is Pelvic Congestion Syndrome?
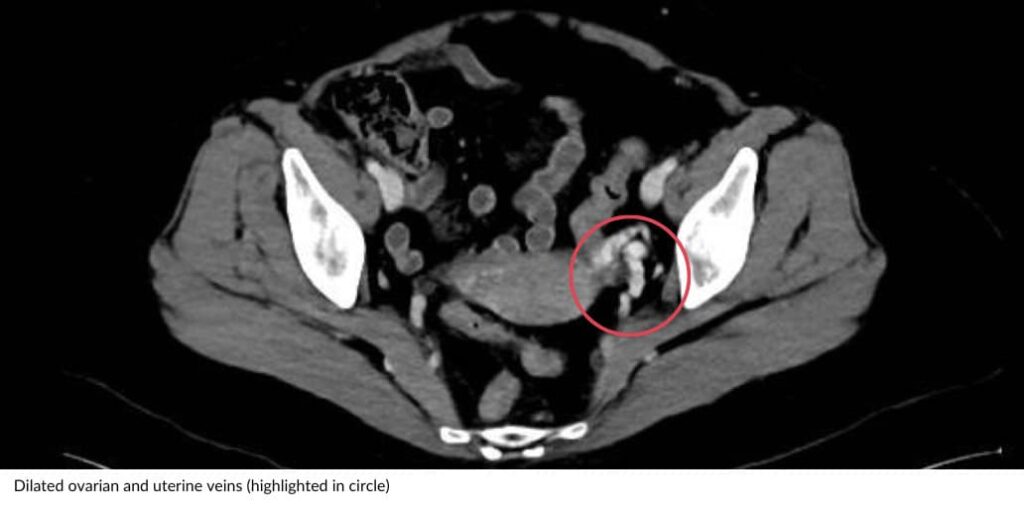
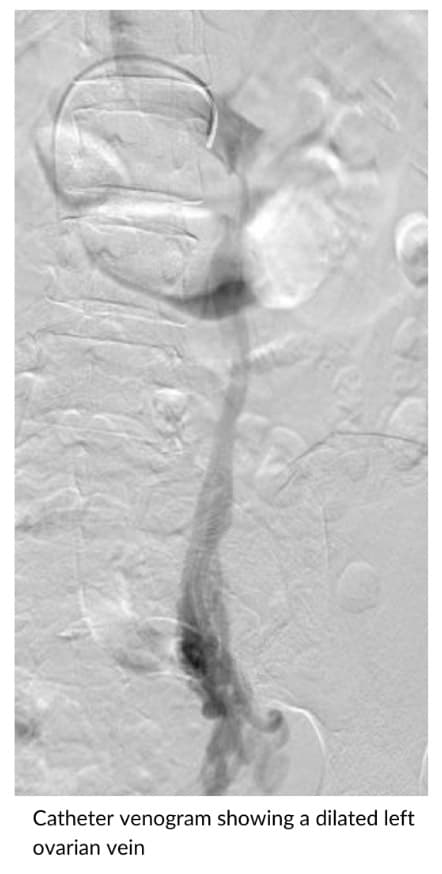
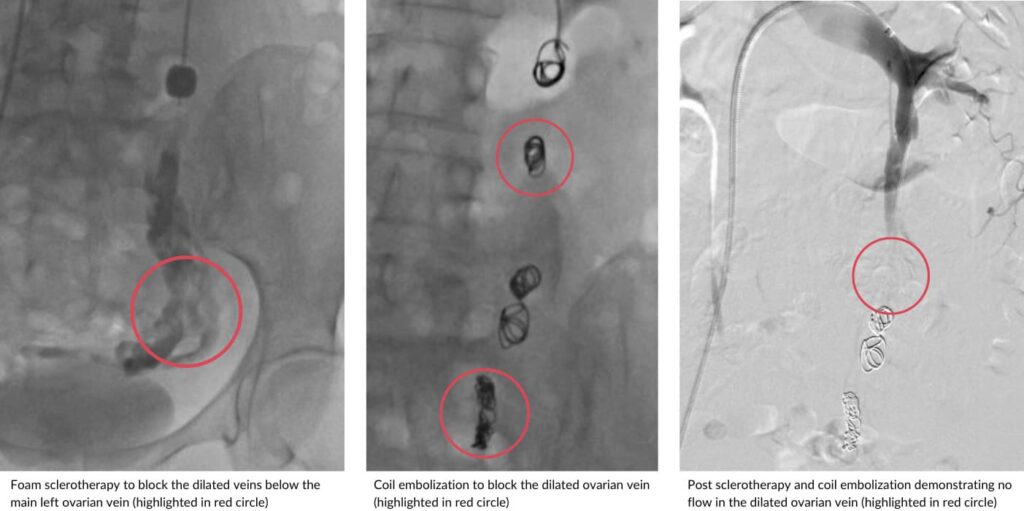
Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS), otherwise known as pelvic venous disease, is a condition underdiagnosed in women and is one of the causes of chronic pelvic pain unrelated to the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. It is caused by “varicose veins” in the pelvis overlying organs, including the uterus, bladder and intestines, leading to venous stasis, venous swelling and twisting, causing the severe pain associated with the condition.
Pelvic congestion syndrome is associated with ovarian vein dilation and can also result in varicose veins in the thigh, buttock and vaginal regions.