Leg swelling, also known as edema, refers to fluid accumulation in the leg tissues, leading to an abnormal enlargement or puffiness. This develops in the feet, ankles, calves, and thighs for various reasons. While some causes of edema are not worrisome, others may be warning signs of more severe conditions such as heart disease or a blood clot.
What Is Edema: Causes & Symptoms of One-Sided Leg Swelling
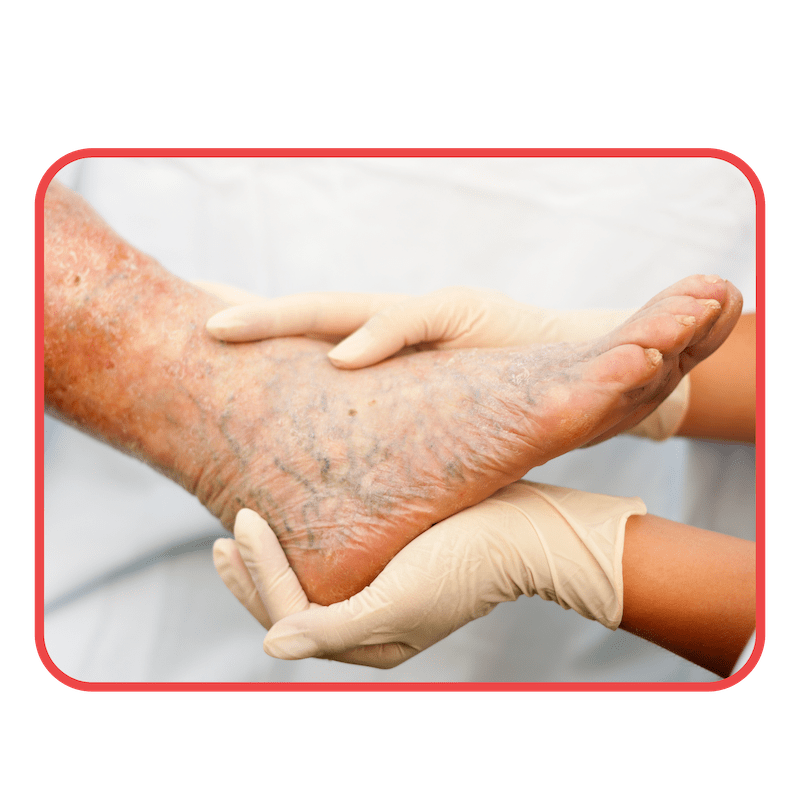
Venous insufficiency is the primary reason for one-sided leg swelling in older individuals. This condition occurs when the valves in the leg veins are damaged or weakened, leading to poor blood flow and fluid retention. The second most frequent cause of leg swelling is an adverse reaction to specific medications. While some are usually associated with heart issues, they only occur 10 to 15% of the time.
Other Causes of One-Sided Leg Swelling
Deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, resulting in swelling, pain, and warmth in one leg.
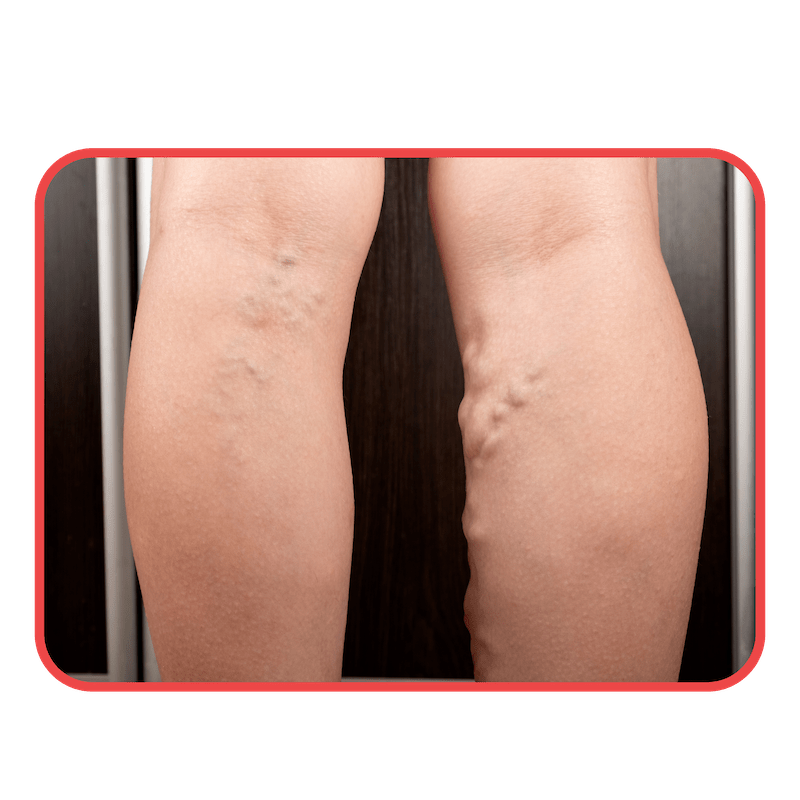
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins, causing swelling and discomfort.

Lymphedema is a chronic condition where the lymphatic system fails to drain fluid from tissues, leading to swelling.
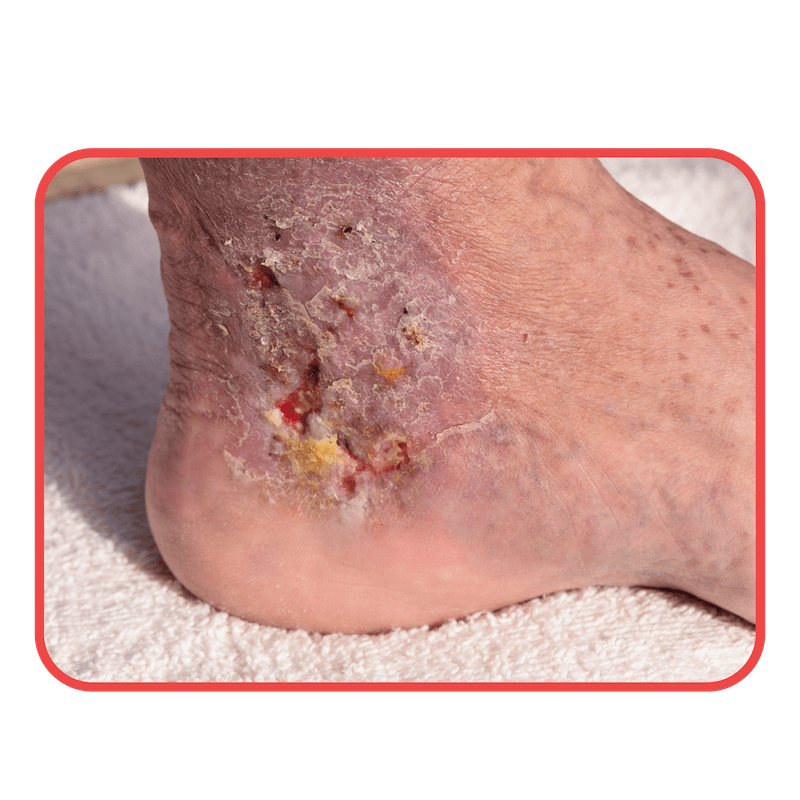
Infections like cellulitis can cause localised swelling, redness, and warmth in one leg.
Injury or trauma to the leg, such as a fracture, sprain, or muscle strain.
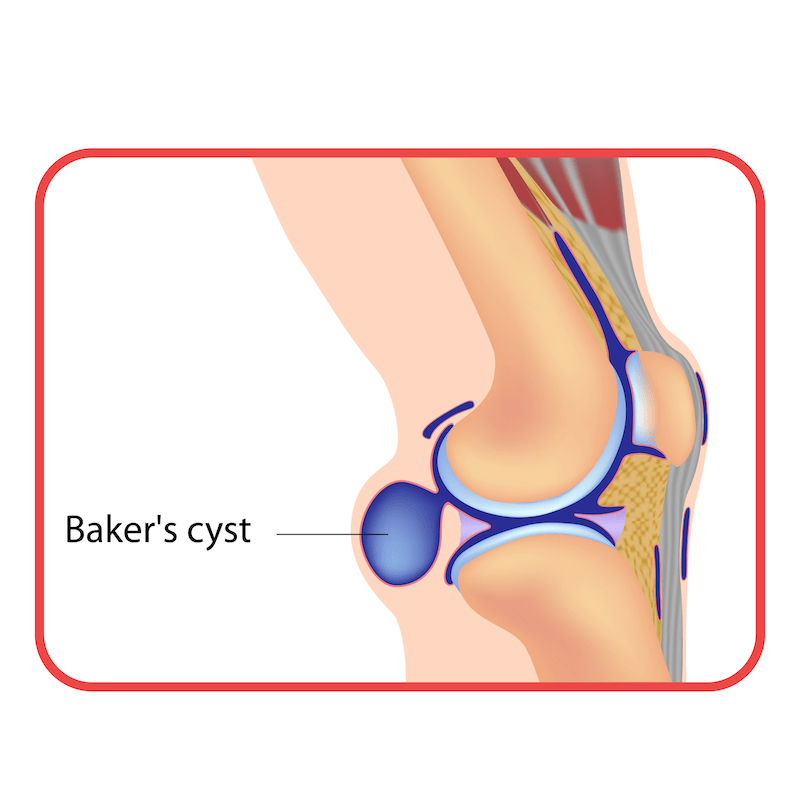
Baker’s cyst or a fluid-filled swelling behind the knee due to osteoarthritis and meniscus tear.
Symptoms of Leg Swelling
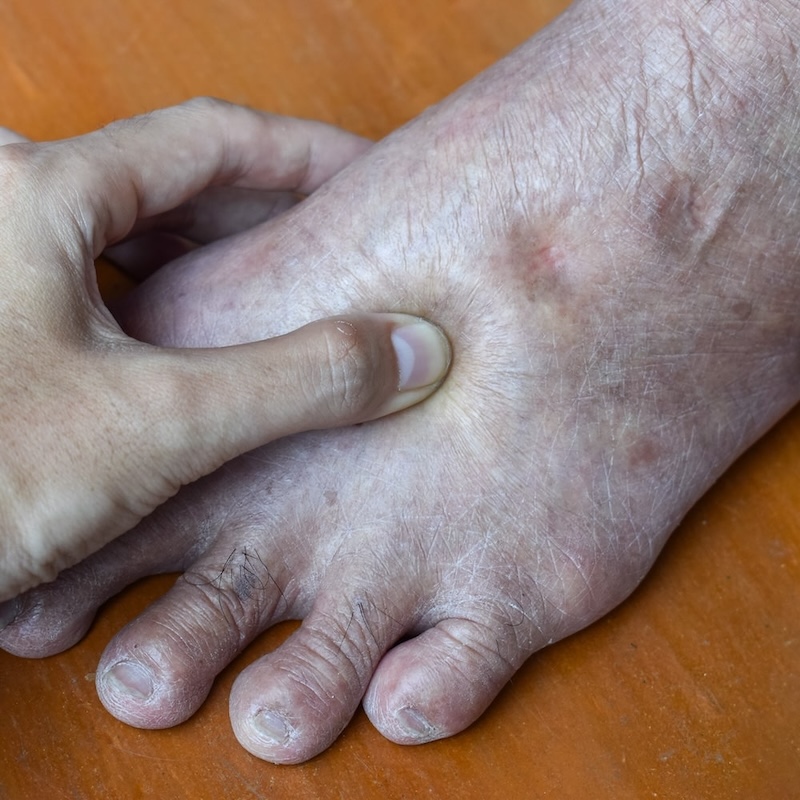
Indents on the skin after removing socks or pant legs
Heavy, numb, or itchy legs

Puffy, stretched, or shiny skin
Tight skin or pain in the affected area
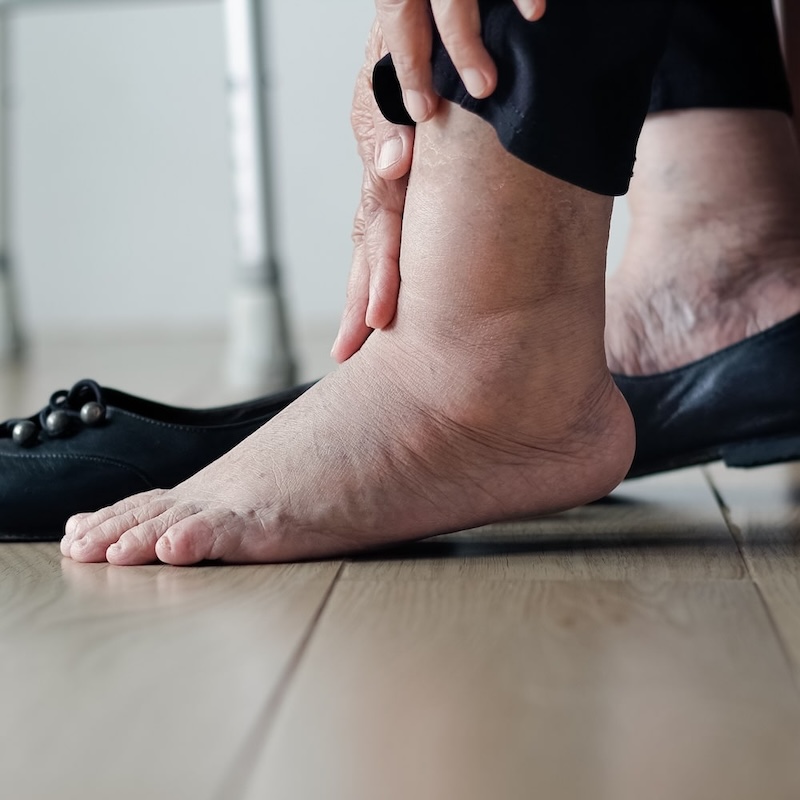
Difficulty putting on or taking off shoes

Difficulty to bend at your ankles
When Should I Be Worried About Leg Swelling?
Leg swelling is a common and benign symptom, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting or from minor injuries. However, certain situations may cause concern and warrant medical attention when leg swelling occurs with the following.
Leg swelling affects daily activities and causes significant discomfort or difficulty with movement.
Sudden and severe leg swelling accompanied by pain, warmth, and redness may indicate a blood clot requiring immediate medical attention.
Persistent leg swelling without improvement from rest, elevation, and home remedies.
Leg swelling with shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood may indicate pulmonary embolism.
Leg swelling with increased redness, warmth, tenderness, and fever may indicate infection.
Sudden or significant weight gain and leg swelling may indicate a systemic issue.
Additionally, edema may signify a more serious complication for individuals with a heart, kidney, or liver disease history. These conditions may increase their risk of fluid retention and leg swelling.
Most leg swelling resolves within a day or two. However, when other symptoms accompany it, assessment from our senior vascular specialists is beneficial to determine the condition’s root cause. We provide a detailed evaluation of your symptoms and perform accurate diagnostic tests to develop a personalised treatment plan.
How to Reduce Edema
Reducing leg swelling with lifestyle changes is possible, especially when you take time to care for yourself. For instance, walking regularly reduces edema due to muscle movement in your legs, which helps pump fluid out of the legs and back towards the heart. This habit prevents blood from pooling and reduces the risk of blood clots.
Here are other ways how to treat edema and stimulate blood flow
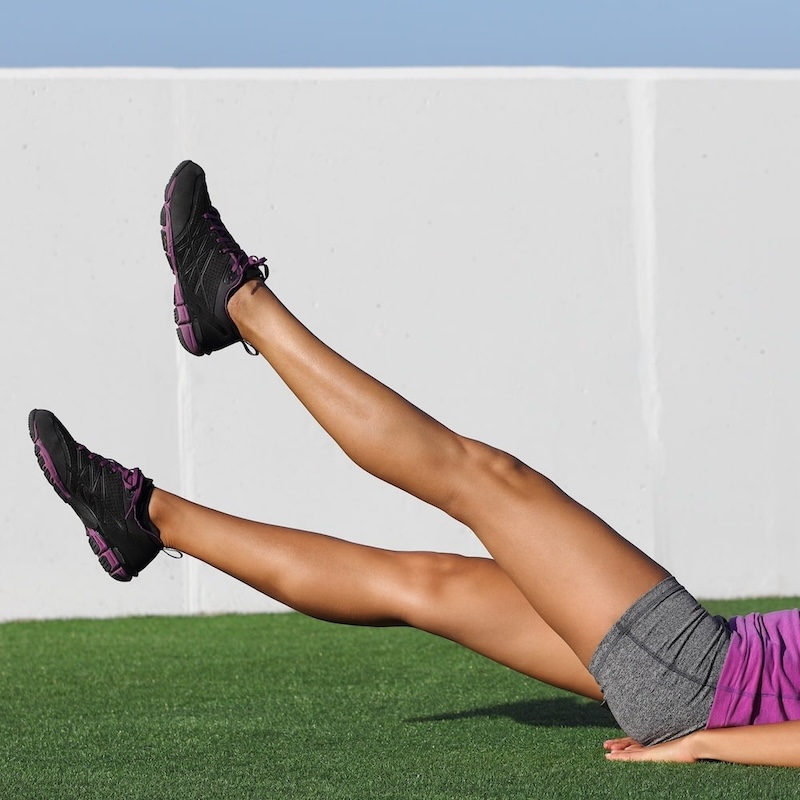

Raise your legs above the level of your heart to drain excess fluid from your legs.
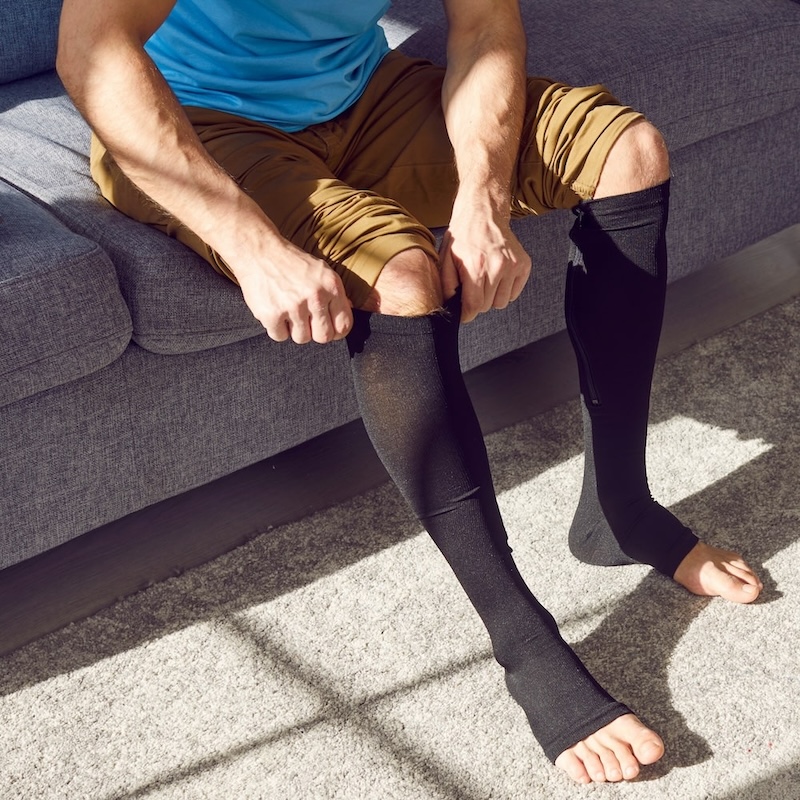

Wear compression stockings or socks for gentle pressure and improved blood circulation.
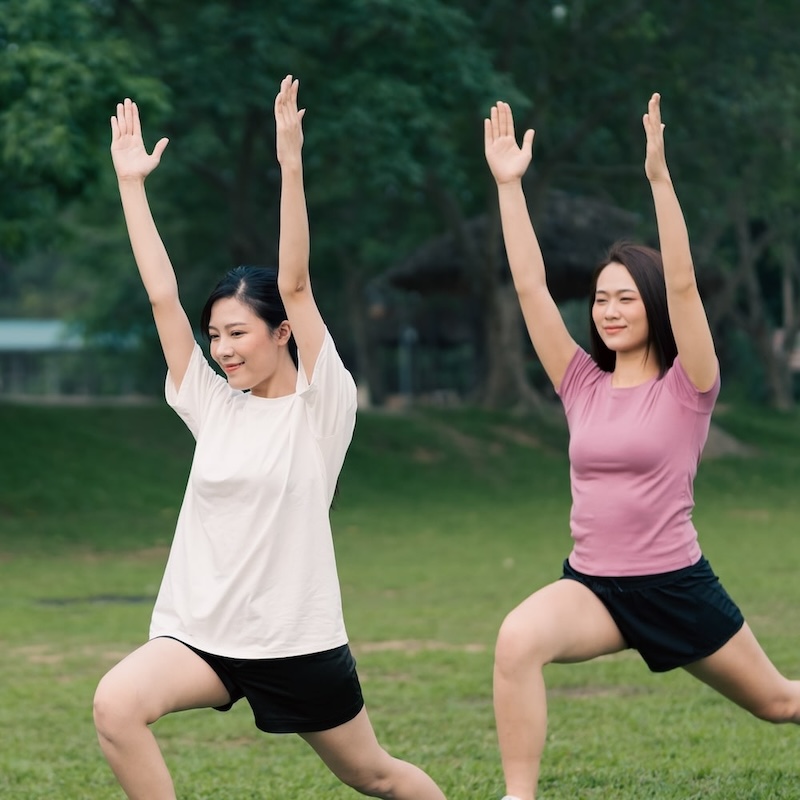

Exercise and movement, such as walking or light activities, to promote blood flow and reduce swelling.
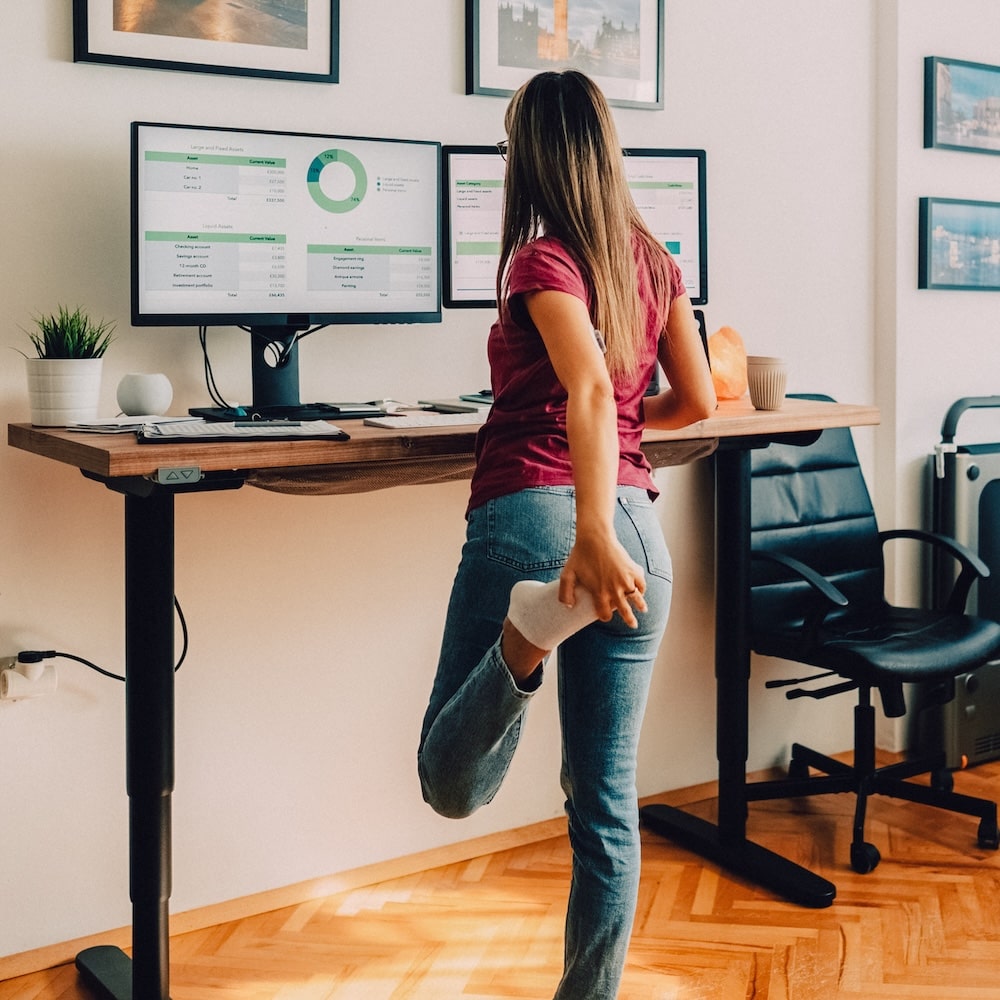

Avoid sitting or standing for long periods without movement.
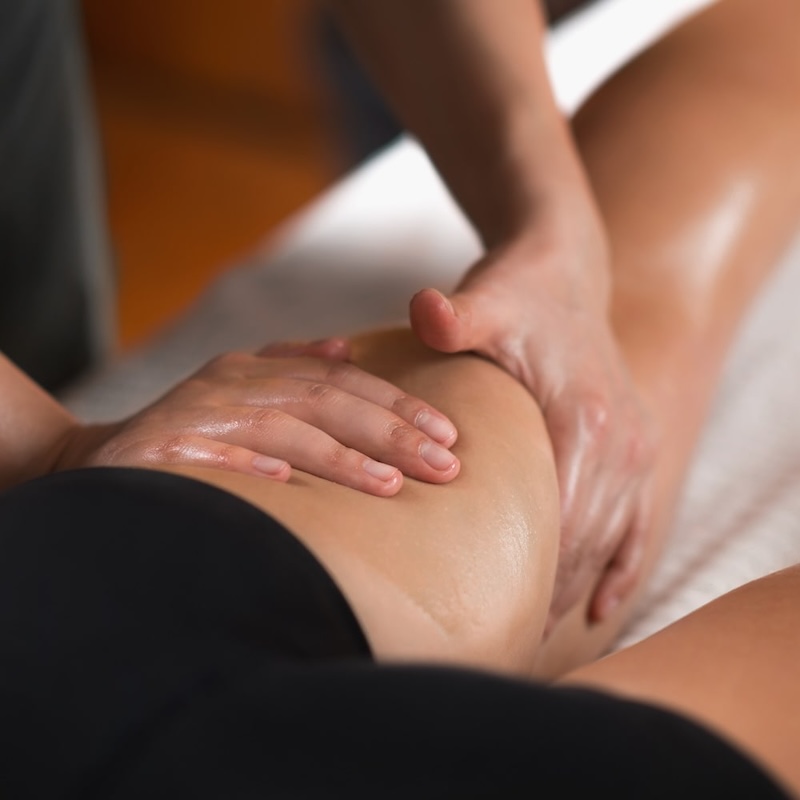

Gently massage the legs using upward strokes towards the heart to stimulate blood flow.
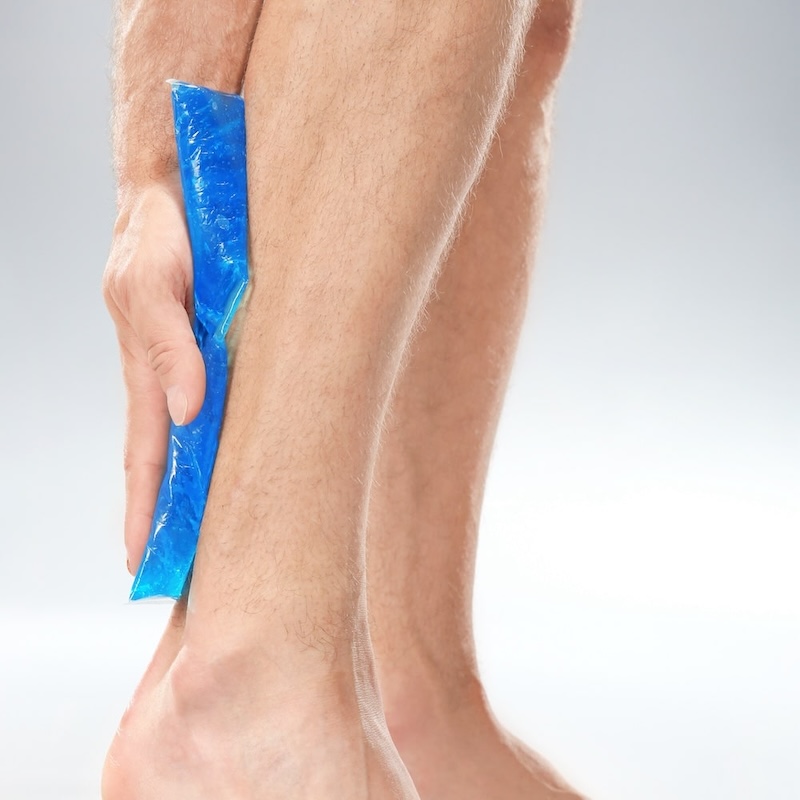
Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth to the swollen areas for 15-20 minutes daily to relieve pain and swelling.
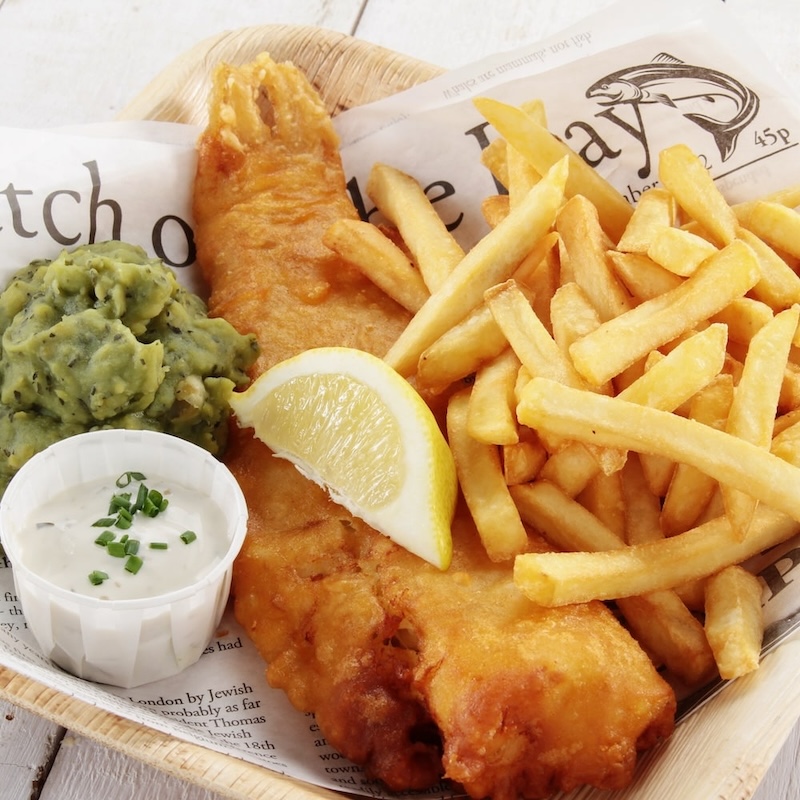

Reduce your consumption of salty foods and processed snacks. High sodium content foods contribute to fluid retention and swelling.
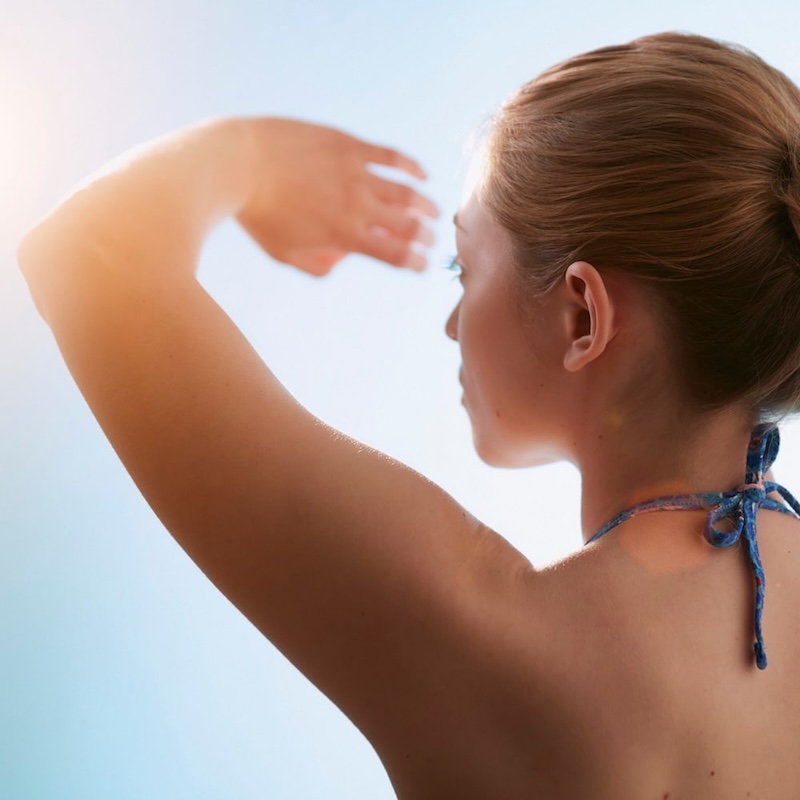

Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and hot baths. Heat causes blood vessels to dilate and increase swelling.
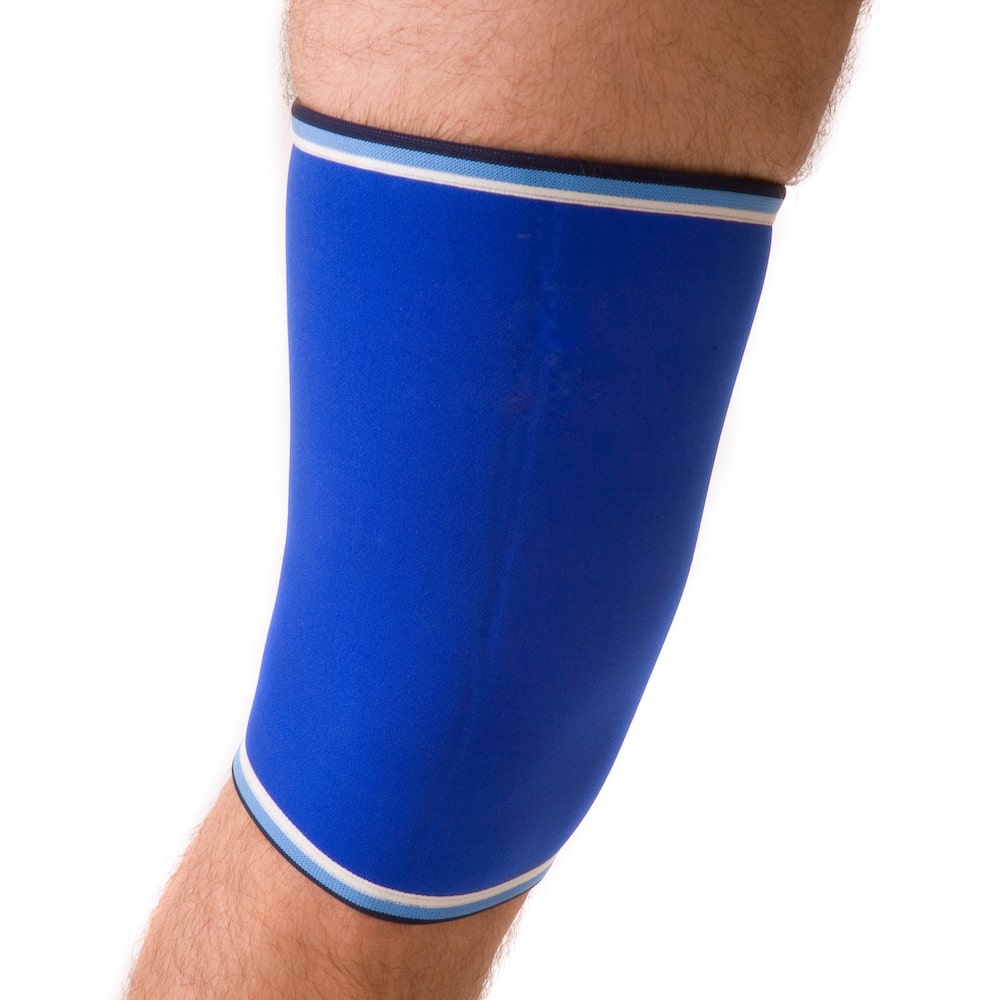
Avoid wearing tight clothing or accessories, such as knee guards or braces, that may restrict circulation and contribute to leg swelling.
Leg Swelling Prevention and Relief: Vascular Solutions Tailored For You
Recognising the nature of leg swelling and its causes is vital in preserving your vascular health. If left unmanaged, edema may worsen health conditions, such as infections, blood clots, and lymphoedema. As a result, early intervention is critical to successful leg swelling prevention and relief.
At the Vascular and Endovascular Clinic (VEC), we’re dedicated to providing patients with effective and personalised solutions for vascular conditions causing edema. By assessing your risk factors, medical history, and the nature of your leg swelling, we develop a tailored treatment plan that suits your condition, including conservative management, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical intervention.
Take action with our early interventions today.









